Jetequip
Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF)
Tangential flow filtration (TFF) is a popular technology in industrial separation, clarification and concentration processes. TFF filtration is also known as cross-flow filtration. This type of filtration is widely used in biotech and the applications are numerous, such as the filtration of monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, insulin, enzymes, IPA, probiotics, bioplastics, algae , biocides, vegetable proteins and many more.
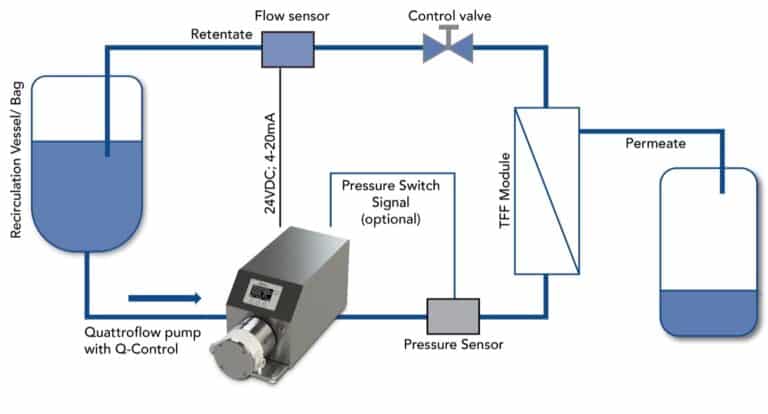
The Process
Tangential flow filtration works by separating cells or molecules based on their size (molecular weight) using a porous membrane operating with tangential flow at the separation surface. Based on membrane pore size, TFF can be divided into microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis
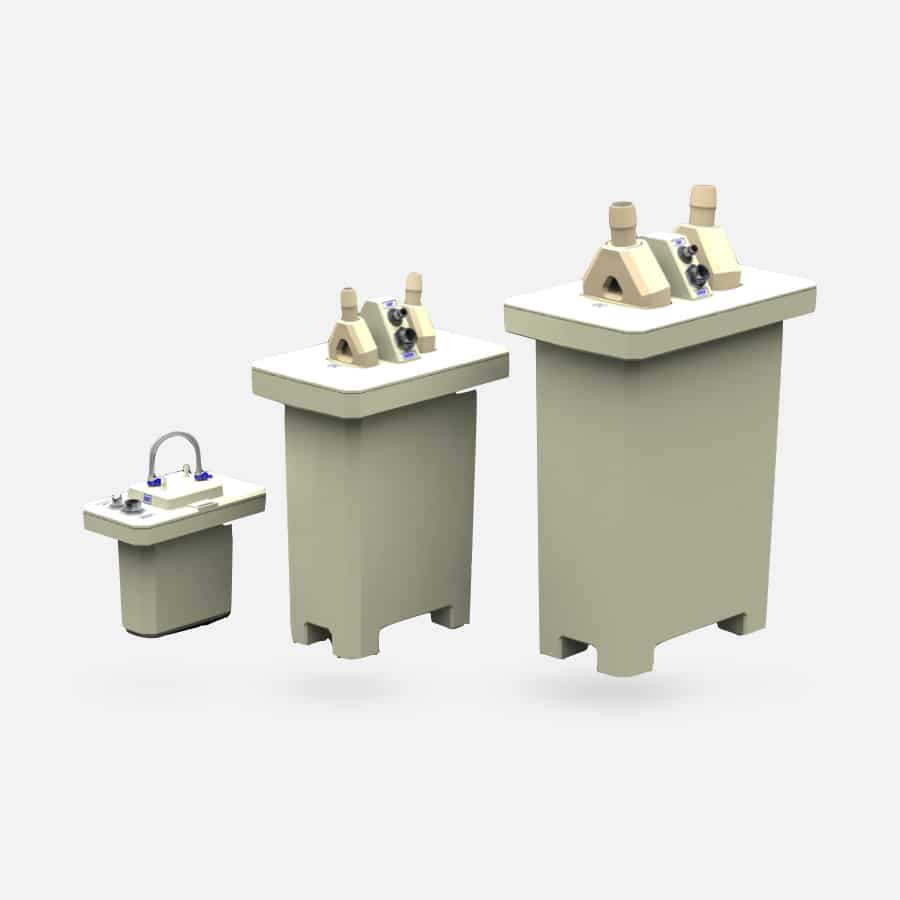
Meet your clean and aseptic
process specialist
Discover our custom-made solutions and modular sanitary equipment. We join forces with our expert partners to develop, design and integrate proven solutions.
The Challenge
There are many challenges in the TFF process, here are some parameters and conditions to pay particular attention to when developing the process:
- Matrix/Composition/Viscosity
- Pumps/Flow/Product Volume
- Shear Stress Sensitivity/Product Physical Properties
- Concentration/Solubility
- Process temperature
- Interface/Operation
- Bioprocess scalability (on all platforms)
- Constancy/Filter life
- Selectivity/Yield
- Downstream Execution
Our solutions
How can a pump be designed to convey extremely delicate biologically active molecules? The solution is in nature itself! Millions of years of evolution developed the perfect device to pump blood that contains albumin, gamma globulins, clotting factors and cells. It is the heart!
See nowThe Advantages
When compared to the features and benefits of Quattroflow pumps, lobe pumps have a variety of operational limitations and shortcomings that do not lead to an optimized production process. The Quattroflow pump advantages include:
- Scalable: High turndown allows multiple flow duties
- Durable: Self-priming (even when running dry)
- Designed for fast maintenance: Seal-less engineering for fast and easy maintenance
- Efficiency: Even with low-viscosity, low-flow applications
- Purity: No metal-to-metal wear, no seals to ensure virtually zero particle generation
- Flexible: Suitable for multiple-use and single-use applications
In addition to the particle generation coming from wear of peristaltic pumps tubing, there are additional disadvantages inherent in peristaltic pumps that could potentially threaten the quality of your process and final product, including:
- Consistency: Low pulsation for high precision
- Tube failure: High mechanical stress can result in tube rupture that can lead to a catastrophic failure, costly product loss, downtime and maintenance.
- Flow rate consistency: With increasing operating time of the tube, mechanical stress changes the hose geometries over time and can lead to an inconsistent flow.
- Particle generation outside the hose: Spallation release may also occur outside the hose. This may compromise the fluid path but also contaminate the external cleanroom environment.
- Pump technology change: Limited flow and pressure capabilities of peristaltic pumps mean changing pump technologies as processes move from process development to cGMP creating scale-up issues.



